How Does Sulfur Valence Work? Simple Answers
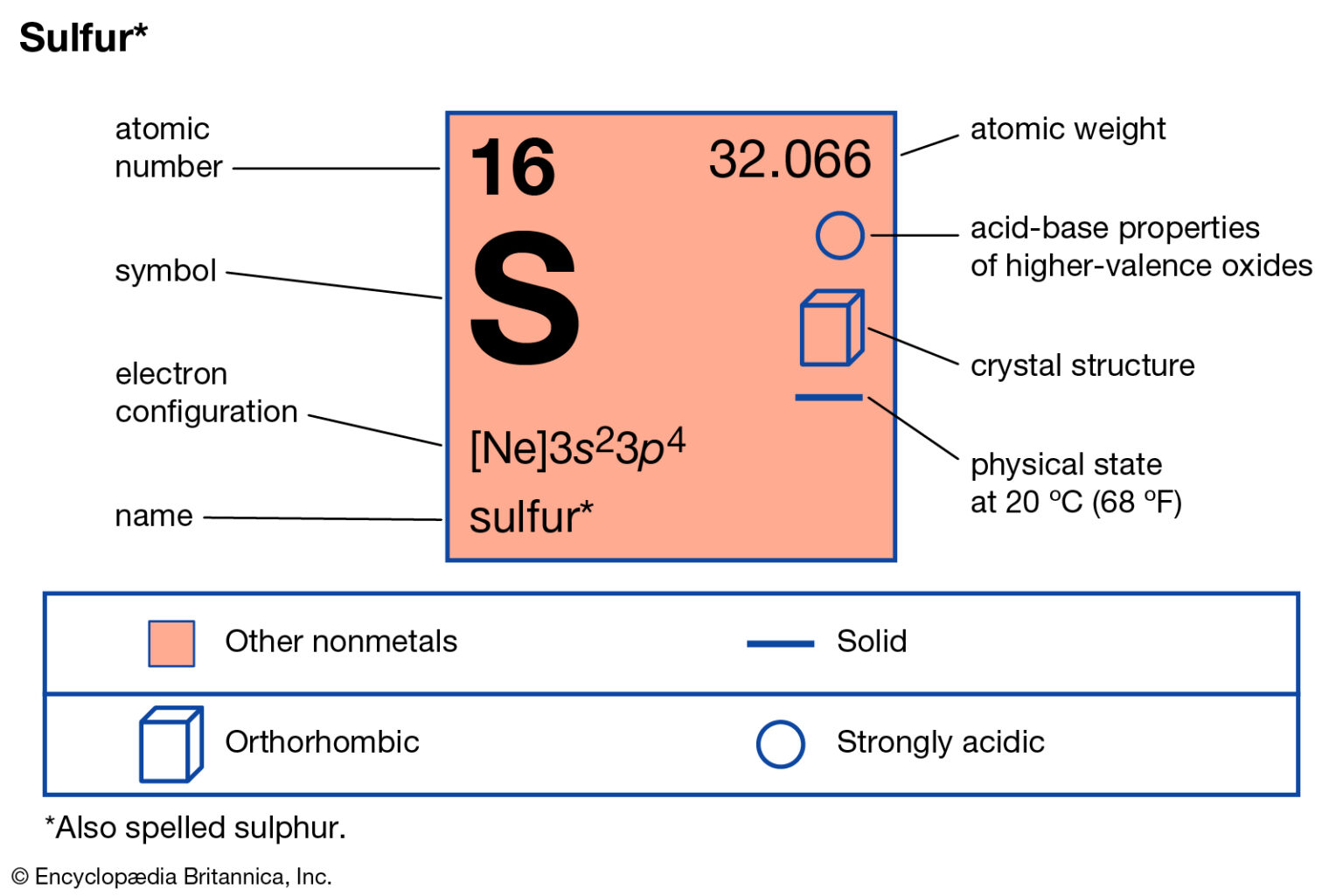
Sulfur is a versatile element that plays a crucial role in various chemical compounds, including amino acids, proteins, and fertilizers. One of the key aspects of sulfur chemistry is its valence, which refers to the number of electrons that an atom of sulfur can gain, lose, or share to form chemical bonds. Understanding sulfur valence is essential to grasp the properties and behaviors of sulfur-containing compounds.
Introduction to Sulfur Valence

In chemistry, valence is a measure of the combining power of an element, which is determined by the number of electrons in its outermost energy level. Sulfur, with an atomic number of 16, has six electrons in its outermost energy level, which can be represented as 3s²3p⁴. This electronic configuration allows sulfur to exhibit a range of valences, from -2 to +6, depending on the chemical environment.
Sulfur Valence States
Sulfur can exhibit several valence states, including:
- -2: In this state, sulfur has gained two electrons to form a stable anion, often referred to as sulfide (S²⁻). This valence state is commonly found in compounds like hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) and sodium sulfide (Na₂S).
- +4: In this state, sulfur has lost four electrons to form a cation, often referred to as sulfur(IV) or sulfite (SO₃²⁻). This valence state is commonly found in compounds like sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and sulfite salts.
- +6: In this state, sulfur has lost six electrons to form a cation, often referred to as sulfur(VI) or sulfate (SO₄²⁻). This valence state is commonly found in compounds like sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) and sulfate salts.
These valence states are not mutually exclusive, and sulfur can exhibit multiple valences in the same compound, depending on the chemical environment. For example, in the compound sulfur dioxide (SO₂), sulfur has a valence of +4, while in the compound sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), sulfur has a valence of +6.
Factors Influencing Sulfur Valence

The valence of sulfur is influenced by several factors, including:
- Electronegativity: The electronegativity of the surrounding atoms or groups can affect the valence of sulfur. For example, when sulfur is bonded to highly electronegative atoms like oxygen or fluorine, it tends to exhibit a higher valence state.
- Coordination number: The coordination number of sulfur, which refers to the number of atoms or groups bonded to it, can also influence its valence. For example, in compounds with a high coordination number, sulfur may exhibit a higher valence state to accommodate the increased number of bonds.
- Chemical environment: The chemical environment, including the presence of other atoms or groups, can also affect the valence of sulfur. For example, in acidic environments, sulfur may exhibit a higher valence state due to the increased availability of protons.
Understanding the factors that influence sulfur valence is crucial to predicting the properties and behaviors of sulfur-containing compounds.
Applications of Sulfur Valence
The unique valence properties of sulfur make it an essential element in various industrial and biological processes. Some examples include:
- Fertilizers: Sulfur is a key component of fertilizers, where it is often used in the form of sulfate or sulfite salts. The valence of sulfur in these compounds determines their reactivity and efficacy as fertilizers.
- Amino acids and proteins: Sulfur is a critical component of amino acids like methionine and cysteine, which are essential for protein synthesis. The valence of sulfur in these compounds affects their reactivity and interactions with other molecules.
- Energy storage: Sulfur is being explored as a potential component of energy storage systems, such as lithium-sulfur batteries. The valence of sulfur in these systems affects their energy density and cycling stability.
In conclusion, sulfur valence is a complex and fascinating topic that plays a crucial role in various chemical and biological processes. Understanding the factors that influence sulfur valence and its applications in different fields can provide valuable insights into the properties and behaviors of sulfur-containing compounds.
| Valence State | Compound | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -2 | Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) | A colorless, flammable gas with a characteristic odor of rotten eggs. |
| +4 | Sulfur dioxide (SO₂) | A colorless, pungent gas used as a preservative and disinfectant. |
| +6 | Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) | A highly corrosive, strong acid used in various industrial processes, including the production of fertilizers and explosives. |

What is the most common valence state of sulfur?
+The most common valence state of sulfur is +6, which is found in compounds like sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) and sulfate salts.
How does electronegativity affect sulfur valence?
+Electronegativity can affect sulfur valence by influencing the electron density around the sulfur atom. Highly electronegative atoms or groups can pull electrons away from sulfur, causing it to exhibit a higher valence state.
What are some common applications of sulfur valence?
+Sulfur valence has various applications in fertilizers, amino acids and proteins, energy storage, and other fields. The unique valence properties of sulfur make it an essential element in these processes.