Lake Effect Snow Forecast

The lake effect snow phenomenon is a significant weather pattern that affects the Great Lakes region, particularly during the winter months. This type of snowfall is caused by the interaction between cold air and the warmer waters of the Great Lakes, resulting in heavy snowfall in certain areas. In this article, we will delve into the world of lake effect snow forecasting, exploring the key factors that influence this weather pattern and the techniques used to predict its occurrence.
Introduction to Lake Effect Snow
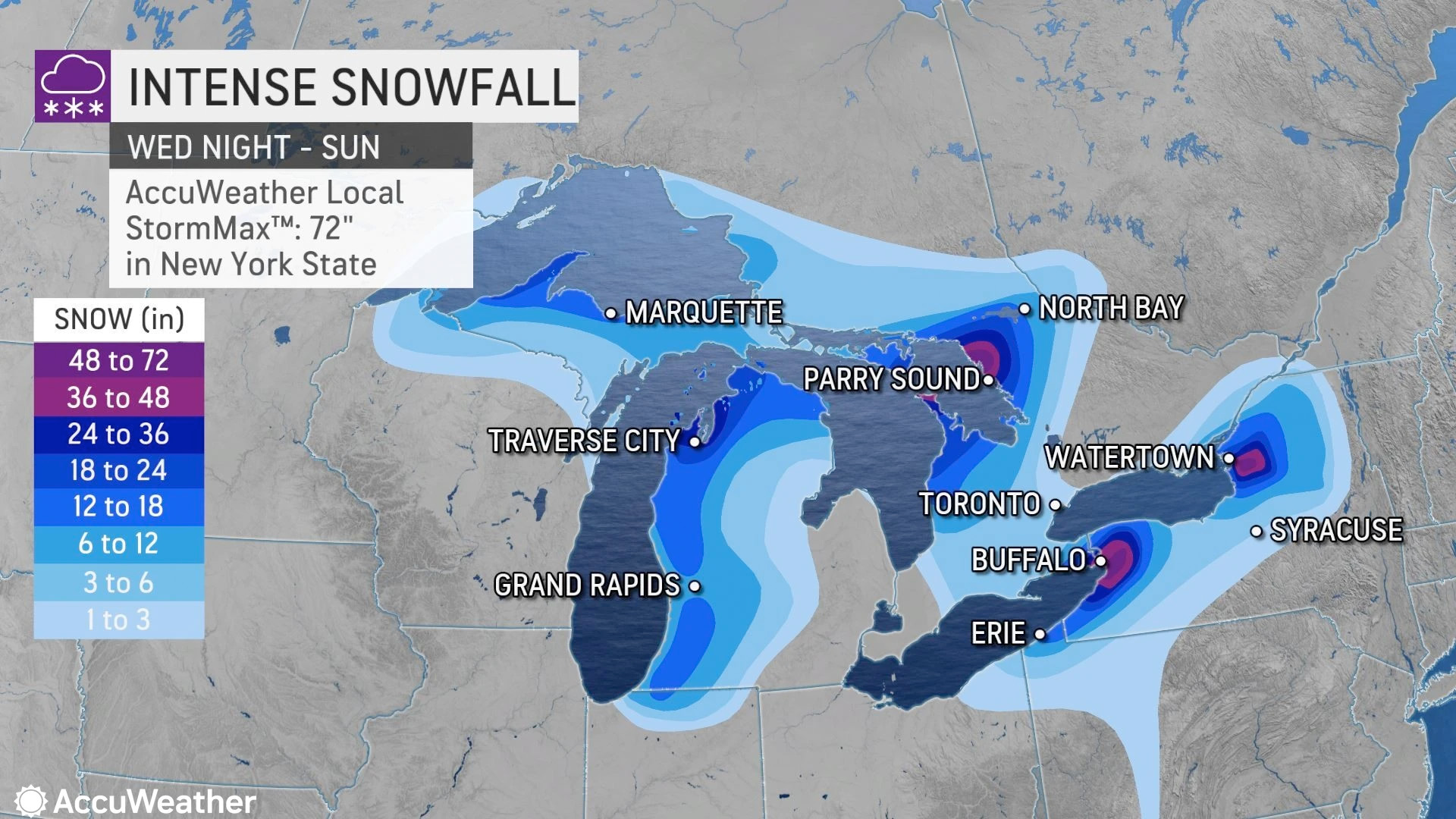
Lake effect snow is a unique weather phenomenon that occurs when cold air passes over the warmer waters of the Great Lakes, causing the water to evaporate and rise into the atmosphere. As the water vapor rises, it cools and condenses, forming clouds and eventually snow. The snowfall is typically heavy and localized, with some areas receiving significantly more snow than others. The lake effect snow belt, which includes regions such as Buffalo, New York, and Erie, Pennsylvania, is particularly prone to this type of weather.
Key Factors Influencing Lake Effect Snow
Several factors contribute to the development of lake effect snow, including the temperature difference between the air and water, wind direction, and the presence of moisture in the atmosphere. A significant temperature difference between the cold air and warm water is necessary to initiate the evaporation process, while a wind direction that allows the air to pass over the lake is crucial for the development of the snow-bearing clouds. Additionally, the presence of moisture in the atmosphere, such as from a previous weather system, can enhance the lake effect snow potential.
| Factor | Importance |
|---|---|
| Temperature difference | High |
| Wind direction | High |
| Moisture in the atmosphere | Moderate |

Lake Effect Snow Forecasting Techniques

Forecasting lake effect snow requires a combination of observational data, computer models, and expertise. Meteorologists use a variety of tools, including satellite imagery, radar, and surface weather observations, to monitor the development of lake effect snow. Computer models, such as the Global Forecast System (GFS) and the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) model, provide valuable guidance on the potential for lake effect snow. Additionally, meteorologists use their knowledge of the local weather patterns and the physics of lake effect snow to refine their forecasts.
Model Performance and Limitations
While computer models have improved significantly in recent years, they still have limitations when it comes to predicting lake effect snow. The models struggle to accurately capture the complex interactions between the atmosphere and the lake, leading to uncertainties in the forecast. Additionally, the models may not always accurately predict the wind direction and speed, which are critical factors in determining the location and intensity of the snowfall.
- Global Forecast System (GFS) model
- European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) model
- North American Mesoscale Forecast System (NAM) model
Case Study: The Buffalo Lake Effect Snow Event of 2014
In November 2014, a significant lake effect snow event occurred in Buffalo, New York, resulting in over 7 feet of snowfall in some areas. The event was caused by a combination of factors, including a strong temperature difference between the air and water, a favorable wind direction, and the presence of moisture in the atmosphere. The storm was well-predicted by computer models, which allowed for timely warnings and preparations to be made.
The event highlighted the importance of accurate forecasting and the need for continued research into the physics of lake effect snow. By improving our understanding of this complex weather phenomenon, we can better predict and prepare for these events, ultimately saving lives and reducing the economic impact.
What is lake effect snow?
+Lake effect snow is a type of snowfall that occurs when cold air passes over the warmer waters of the Great Lakes, causing the water to evaporate and rise into the atmosphere, resulting in heavy snowfall in certain areas.
What are the key factors that influence lake effect snow?
+The key factors that influence lake effect snow include the temperature difference between the air and water, wind direction, and the presence of moisture in the atmosphere.
How is lake effect snow forecasted?
+Lake effect snow is forecasted using a combination of observational data, computer models, and expertise. Meteorologists use satellite imagery, radar, and surface weather observations to monitor the development of lake effect snow, and computer models provide valuable guidance on the potential for lake effect snow.
